Translation Tutorial
Translation
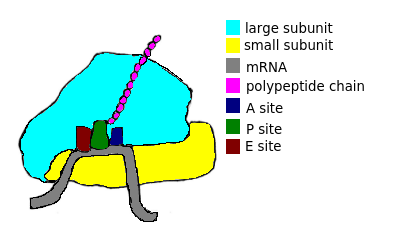
Translation occurs when mRNA enters the cytoplasm and enters a protein called the ribosome.Ribosomes
They are a protein that read mRNA and create polypeptide chains.They consist of two subunits, one is called the large subunit and the other is called the small subunit. During translation, mRNA resides between the two subunits.
Within the ribosome, there are three sites for the tRNA (transfer RNA) to enter and build a polypeptide chain.
They are called the;
- A site (aminoacyl binding site)
- P site (peptide binding site)
- E site (exit site)
 Like transcription, there are the three stages;
Like transcription, there are the three stages;
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
- Initiation
- The 5' cap, which was placed on the mRNA before exiting the nucleus is recognized by the ribosome. The start codon (AUG) which codes for the amino acid methionine is also recognized by the ribosome.
- To produce a polypeptide chain, mRNA is read by the ribosome in a 5' to 3' direction. For each codon, a new amino acid is added.
- Elongation
- The initiator tRNA with the amino acid methionine enters the P site.
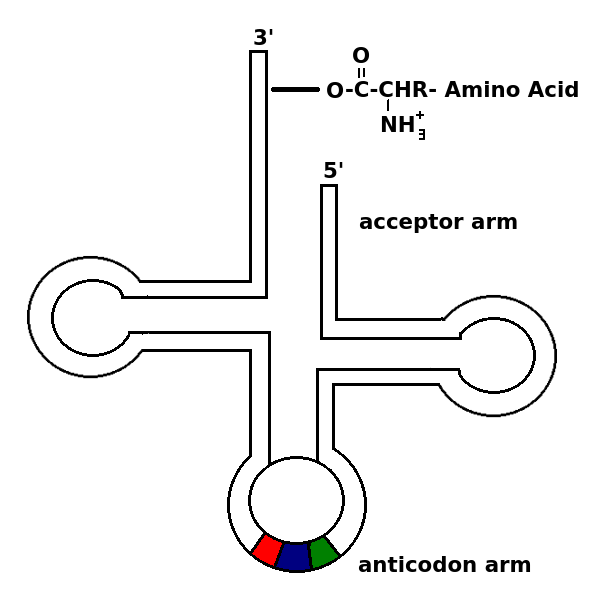
- The second tRNA with the correct bases on the anticodon arm then binds with the codon of the A site.
- Peptidyl transferase catalyses the bond between the two amino acids.
- The ribosome moves along the mRNA, to the next codon, emptying the A-site and moving the initiator tRNA to the E-site.
- As the ribosome moves to another codon, the tRNA is released.
- This cycle continues until the stop codon is encountered.
- Termination
- When the stop codon (UAG, UGA, UAA) is encountered, the polypeptide chain production is terminated. No amino acid is coded for.
- A protein, called the release factor, aids in the removal of the polypeptide chain from the ribosome.
- Then the large subunit and the small subunit of the ribosome fall off of the mRNA.
- The polypeptide chain then folds into a protein.
Codon: A series of three nitrogenous bases which code for an amino acid.
Transfer RNA Diagram
Note: During production, some modifications are made. Sugar or phosphate groups may be added to certain amino acids. In addition, enzymes may cleave the polypeptide chain at certain areas.